22 JUNE NIE TOI
" TO DEVELOP CREATIVITY, INNOVATION, LIFE SKILLS, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LANGUAGE SKILLS APART FROM CAREER COUNSELLING AND PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT” " PLUS TO CATER ALL THE INFORMATION NEEDS OF KVS TEACHERS AND STUDENTS. WE ACKNOWLEDGE OUR SINCERE THANKS TO ALL KNOWN & UNKNOWN CONTRIBUTORS ON WEB, WHERE SOURCE IS UNKNOWN / UNTRACEABLE/LINKED (THIS IS AN ERSTWHILE " KV REWARI LIBRARY BLOG TILL 30.09.2019. " AND KV ITBP BHANU LIBRARY BLOG TILL 30.05.2025.)
Search This Blog
LIB
- HOME- LIB-BLOG
- E BOOKS
- E MAGAZINES
- E-NEW PAPERS
- LIBRARY
- MAG-SUBSCRIPTION
- STD-ORIENTATION
- BEST SCHOOL4MY KIDS
- CAREER-SIKSHA
- KVS ADMISSIONS
- KVS CIRCULARS
- ABOUT KVS
- JAGO GRAHAK
- LIB. ANNUAL REPORT
- VICKAS -YOUTUBE
- SUGAMAYA
- OLD Q.P. OLYMPIADS
- BHARAT KOSH
- NMEICT
- APAAR
- NASA
- SATHEE-GK & Current Affairs
- ONLINE BOOK REVIEW
- DIGITAL VOCATIONAL BOOKS
- DIKSHA
- NISTHA
- SCHOLASTIC WORLD
- CALCULATOR
- GLOBAL PUBLISHERS
- GLOBAL AUTHORS
- GLOBAL REFRENCE LINKS
- KVS LIB POLICY 2012
- LIB GUIDELINES KVS-2015
- NATIONAL PORTAL OF INDIA
- NCERT AUDIO TEXT BOOKS
- PROJECT INCLUSION
- SAMAGAM-KVS
- PIMS-KVS
- LIB ANNUAL REPORT 2023-24
- EG 4.0 LIB. OPAC
- EG 4.0 LOG IN
- EG 4.0 DIGITAL LIB.
- EG 4.0 KV CLUSTER-3
- EG 4.0 MOB. APP
- 9000 DIGITAL MAGAZINES BY EDZTER
- URKUMD
- DrillBit
- SIP - SWOT
- UBI FEE PORTAL
Monday, 30 June 2025
YOGA DAY 2025 - JUNE 21
 BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
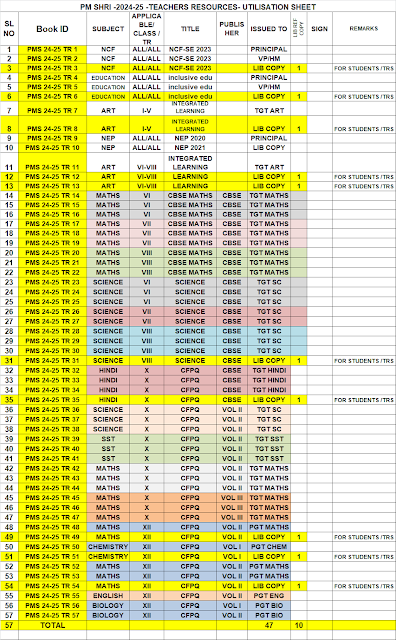
PM SHRI -2024-25 -TEACHERS RESOURCE UTILISATION SHEET
 BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
Sunday, 29 June 2025
Career in E commerce
- What they cover:These courses typically cover topics like digital marketing strategies, e-commerce platform management (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce), online store setup, order fulfillment, customer relationship management, and analytics.
- Learning formats:Courses are available online, offering flexibility for students and working professionals.
- Examples:
- Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate: Offered through Coursera, this certificate focuses on foundational skills for entry-level roles.
- Certificate Program on Ecommerce Entrepreneurship: This program from EDII focuses on initiating an e-commerce business.
- DataTrained's PG Program in E-Commerce and Business Analytics: This program includes a 3-month internship and industry projects.
- Value:Internships provide hands-on experience in a real-world e-commerce setting, allowing you to apply your classroom knowledge and develop practical skills.
- Opportunities:Internships can be found in various areas, including marketing, sales, operations, and customer service.
- Finding internships:Platforms like Internshala and company websites are good resources.
- Examples:
- Internshala: Lists various e-commerce internships, including those with a work-from-home option.
- Kaashiv's Ecommerce Online Internship: Offers an online internship with video lectures and practice problems.
- Best of both worlds:Many certificate programs include internships as part of the curriculum or offer placement assistance.
- Benefits:This combination provides a strong foundation in e-commerce principles and practical experience, increasing your employability.
- Example:DataTrained's program integrates a 3-month internship and industry projects, while EDII's program includes handholding support for two years post-completion.
- Check local job boards like Internshala for e-commerce internships in the area.
- Consider online programs that offer placement assistance or have partnerships with companies in the region.
- Look for courses that cover digital marketing and e-commerce, as these skills are highly sought after in the current job market.
 BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
Top 6 high-paying careers to pursue
Physicians and surgeons
Physicians and surgeons top the list of high-paying American careers. The BLS reports a median wage of $239,200 (approximately ₹2 crore) or more annually for this group.
Subspecialties such as pediatric surgery, cardiology, orthopedic surgery, radiology, and anesthesiology can earn even higher average incomes, ranging from $300,000 to $450,810 (ranging from ₹2.5 crore to ₹3.8 crore).
Dentists and orthodontists
Dental specialists such as orthodontists and oral and maxillofacial surgeons also rank among the highest earners. Median annual wages for dental specialists exceed $239,200 (approximately ₹2 crore), according to BLS data.
Aspiring dental professionals must complete a professional dental degree followed by advanced training in a chosen specialty. The demand for dental specialists continues to grow due to increased emphasis on preventive care and overall oral health, making it a financially and professionally rewarding career choice.
Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialise in mental health. They earn a median annual wage of $239,200 (approximately ₹2 crore) as per the BLS. Their role includes diagnosing and treating mental illnesses and prescribing medications. With increasing focus on mental health care and greater awareness around mental wellness, the need for qualified psychiatrists continues to rise steadily.
Computer and information systems managers
In the technology sector, leadership positions in information systems are highly lucrative. BLS data shows that these managers earn a median annual wage of $169,510 (approximately ₹1.42 crore) as of May 2024.
As companies continue to emphasise cybersecurity, and data management, demand for these professionals keeps growing. The field offers a clear pathway for students with degrees in computer science, information technology, or related fields.
Financial managers
Leadership roles in finance offer high earning potential and steady demand. Financial managers earn a median salary between $134,180 and $156,100 (approximately ₹1.12 crore to ₹1.30 crore) depending on the industry. They are responsible for budgeting, financial planning, and investment management.
Students with degrees in finance, economics, or accounting can enter the field and later obtain credentials such as MBA to enhance career growth in sectors including banking, investment, or corporate finance.
source :Top 6 high-paying careers to pursue in the USA by Apeksha Tanwar
 BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
Thursday, 26 June 2025
ROAD SAFETY & CAREER EDUCATION PROGRAMES IN GOVT. SCHOOLS OF HARYANA
 BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
Curriculum and handbook of AI is available on CbSE Academic Website. Links are attached herewith
Class IX AI Handbook 2024_26-04-24.docx
cbseacademic.nic.in/web_material/Curriculum21/publication/secondary/Class10_Facilitator_Handbook.pdf
AI_Facilitators_Handbook_VI.pdf
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE INTEGRATION ACROSS SUBJECTS FOR CBSE CURRICULUM
 BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
Copyright issues in Digital Era
IPR stands for Intellectual Property Rights.
It’s a fancy way of saying “legal protection for your
creations.” Whether you invent a gadget, write a book, design a logo, compose a
song, or develop software—IPR helps ensure that others can’t just copy or
profit from your work without permission.
There are
different types of IPR, each protecting different kinds of creations:
- Copyright protects original works like
books, music, films, and art.
- Patents – protect inventions and
technical innovations.
- Trademarks – protect brand names, logos, and
slogans.
- Design rights – protect the look and shape of a
product.
- Trade secrets – protect confidential business
information, like secret recipes or algorithms.
The formal legal framework for Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) in
India began during the British colonial era. While
traditional forms of protecting knowledge existed earlier, it was under British
rule that structured laws were introduced:
·
Patents: The first Indian
patent law was enacted in 1856, modeled after British law.
·
Copyrights: The Indian
Copyright Act was introduced in 1914, based on the UK
Copyright Act of 1911.
·
Trademarks: Though trademarks
were protected under common law earlier, the first comprehensive Trade
Marks Act came into force in 1940.
Post-independence, India revamped its IPR laws to align with international
standards, especially after joining the World Trade Organization (WTO)
and signing the TRIPS Agreement in 1995
India has a well-developed legal framework for protecting intellectual
property, with several key laws currently in force:
·
The Patents Act, 1970 (amended
multiple times, most recently in 2024): Governs the granting of patents for
inventions and outlines the rights of patent holders.
·
The Copyright Act, 1957:
Protects original literary, musical, dramatic, and artistic works, as well as
cinematographic films and sound recordings.
·
The Trade Marks Act, 1999:
Provides for the registration and protection of trademarks for goods and
services.
·
The Designs Act, 2000: Protects
the visual design of objects that are not purely utilitarian.
·
The Geographical Indications of Goods
(Registration and Protection) Act, 1999: Safeguards products that have
a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation due to
that origin (like Darjeeling tea or Mysore silk).
·
The Protection of Plant Varieties and
Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001: Recognizes and protects the rights of plant
breeders and farmers.
·
The Semiconductor Integrated Circuits
Layout-Design Act, 2000: Protects the layout designs of integrated
circuits.
Copyright issues in Digital Era
1.
INTRODUCTION :
The
digital era has transformed how we create, share, and consume content—and with
that has come a whole tangle of copyright complexities. Here's a quick
breakdown of key issues swirling around today:
1. Easy Duplication and Distribution :Digital content can
be copied and spread globally with a single click, often without the creator's
permission. Think music, videos, photos, articles—anything that can go online
can be duplicated.
2. User-Generated Content (UGC) :Platforms like
YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram thrive on user creativity, but they often dance
on the edge of copyright infringement when users remix, mash up, or use
copyrighted materials without proper licensing.
3. Digital Rights Management (DRM) :To protect content,
creators and companies use DRM tools. While these guard against piracy, they
can also restrict legitimate usage, like making backups or using content across
devices.
4. Fair Use Confusion: “Fair use” allows
limited use of copyrighted material for commentary, criticism, education, and
parody, but it’s notoriously vague—and navigating it without legal expertise
can be risky.
5. AI and Copyright : With AI generating
art, text, and music, who owns the final product? And what about the data it's
trained on—does that violate copyright if it includes protected content?
6. International Challenges: Copyright laws vary
wildly from country to country. What’s protected in one nation may not be in
another, complicating enforcement across borders.
2.
Copyright :is
a legal right that gives creators control over how their original works—like
books, music, films, software, and artwork—are used and shared. It protects
the expression of ideas, not the ideas themselves.
Here’s
the gist:
- If you create something original
and fix it in a tangible form (like writing it down or recording it), you
automatically own the copyright.
- This gives you exclusive rights to
reproduce, distribute, perform, display, or license your work.
- Others need your permission to use
it—unless their use falls under exceptions like fair use.
3.
Copyright law officially: came into being with the Statute of Anne in
1710 in Great Britain. It was the first law to recognize the rights of
authors over their literary works, rather than granting control solely to
printers or publishers.
Before
that, printing was regulated through royal privileges and monopolies,
especially by groups like the Stationers' Company in England. But the Statute
of Anne marked a turning point—it aimed to encourage learning by giving authors
exclusive rights to their creations for a limited time.
4.
The Copyright Act of 1957 is the primary legislation governing
copyright law in India. Enacted on 4th June 1957, it was designed
to consolidate and modernize the laws relating to copyright, replacing earlier
colonial-era statutes. Here's a quick overview of its key features:
4A. 📘 What It
Covers :The
Act protects original works in categories such as:
Literary works (books, articles,
software)
Musical works
Artistic works (paintings, photographs, architecture)
Cinematographic films
Sound recordings
Dramatic works
4 B 🛡️ Rights
Granted: It
gives creators exclusive rights to:
Reproduce the work
Distribute copies
Perform or display the work publicly
Create adaptations or translations
License or assign rights to others
4 C. ⚖️ Duration of
Protection:
For most works: Lifetime
of the author + 60 years
For films, sound recordings, and anonymous works: 60 years from
publication
4. D 🔄 Amendments
The Act has been amended several times
to keep up with technological changes, most notably in 1994 and 2012, most notably in 1994 and 2012,
5. 📝
Step-by-Step Copyright Registration Process in India
1. Identify the Type of Work Choose
the category your work falls under—literary, musical, artistic,
cinematographic, software, etc.
2. Create an Account on the
Copyright Office Website Visit the Copyright Office of India and
register for an account to begin the application process.
3. Fill Out the Application
(Form XIV) Complete the online form with details about the work and the
applicant. You’ll also need to upload a scanned signature and a copy of the
work.
4. Pay the Fee Submit the
prescribed fee online. The amount varies depending on the type of work.
5. Submit the Application Once
submitted, you’ll receive a diary number as proof of submission.
6. Waiting Period (30 Days) There’s
a mandatory 30-day waiting period to allow for any objections.
7. Examination by the
Registrar If no objections are raised, the Registrar examines the
application. If everything checks out, the work is registered.
8. Issuance of Certificate Once
approved, you’ll receive a certificate of registration and your work will be
entered into the Register of Copyrights.
You
can find a detailed guide on the IndiaFilings website or explore the
official Copyright Office portal for forms and FAQs.
📤 What Happens When You Upload
Content
When
you upload something online (to YouTube, Instagram, a blog, etc.), you're
essentially publishing it to a global audience. If that content includes
copyrighted material—like someone else’s song, artwork, or video clip—you could
be infringing on their rights.
6. ⚠️ Key Copyright Implications
- Unauthorized Use: Uploading copyrighted content
without permission can lead to takedown notices, account suspension, or
even legal action.
- Content ID & Detection: Platforms like YouTube use
automated systems to detect copyrighted material. If flagged, your content
might be demonetized, muted, or removed.
- Fair Use Confusion: Even if you think your use is
“fair” (like for education or commentary), it’s not always clear-cut and
can still be challenged.
- Moral Rights: In some countries, even if you
credit the creator, uploading altered versions of their work can violate
their moral rights.
7. ✅ Best Practices
- Use original content or
works licensed under Creative Commons.
- Always credit the creator and
check the license terms.
- Consider using royalty-free
libraries for music, images, and video.
- If in doubt, get written
permission or a license.
- For a deeper dive into these
issues, you can check out this Legal Vidhiya article on digital
copyright or analysis on copyright infringement in the digital
world.
You
can read the full article titled "Issues in Digital
Copyright" on Legal Vidhiya’s website.
It
offers a comprehensive look at how digital technology has reshaped copyright
law, covering:
- The rise of online piracy and
its impact on creators
- Challenges with enforcement across
borders
- The role of Digital Rights
Management (DRM) and AI-powered monitoring
- Legal frameworks like the Digital
Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA)
- The importance of Creative
Commons licensing and public awareness
- Emerging tech like blockchain and virtual reality in copyright protection
8. 🌐 What Is Creative Commons
Licensing?
Creative
Commons licenses allow creators to:
- Let others use their work with
conditions (like giving credit or not using it commercially).
- Choose from six main license
types, ranging from the most open (CC BY) to the most restrictive (CC
BY-NC-ND).
- Even dedicate their work to the
public domain using CC0, meaning no rights reserved.
§
Creative
Commons (CC) licenses come in six main types, offering a spectrum from the most
permissive to the most restrictive in terms of how content can be used. Here
they are:
§ Each one balances creators'
desire to share with their need for control in a slightly different way.
You
can explore the full range of licenses on Creative Commons' official site.
·
CC BY – Attribution: The most open license.
You can copy, modify, distribute—even commercially—as long as you credit the
creator. Example: "Open Access" by Peter
Suber – a foundational book on the open access movement, published by MIT
Press.
·
CC BY-SA – Attribution-ShareAlike:
Same freedoms as CC BY, but your derivative works must be licensed under
identical terms. (Think: remix culture and Wikipedia Example: Wikipedia –
all articles across its many language editions are licensed under CC BY-SA,
encouraging remixing and reuse with the same license.
·
CC BY-ND – Attribution-NoDerivatives:
You can reuse and redistribute the work, even for commercial purposes,
but no changes are allowed. Example: The
Art of Unix Programming by Eric S. Raymond – shared under CC BY-ND,
allowing redistribution without modification.
·
CC BY-NC – Attribution-NonCommercial:
Others can remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially. They must
still give credit, but they don’t have to license their modified work under the
same terms. Example: Free Culture by Lawrence
Lessig – a seminal work on copyright and creativity, licensed for
non-commercial use with attribution.
·
CC BY-NC-SA – Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike:
You can modify and share the work non-commercially, but your new creations must
carry the same license, and you must give attribution. Example: Little
Brother by Cory Doctorow – a popular young adult novel available for
non-commercial remixing under the same license.
·
CC BY-NC-ND – Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives:
The most restrictive license. You can download and share the work with credit,
but no changes and no commercial use. Example: Move
Under Ground by Nick Mamatas – a horror novel mashup that can be
shared non-commercially but not altered.
9.
✅ Copyright Dos: Here’s
a handy guide to the dos and don’ts of copyright, especially
relevant in today’s digital world:
- Do ask for permission before using someone else’s
work—whether it’s for commercial or personal use.
- Do give proper credit to the original creator when
using their content, even if it’s allowed under fair use.
- Do use public domain or Creative
Commons-licensed materials when available—they’re free to use, but still
check the terms.
- Do register your own original work to strengthen your legal
rights and make enforcement easier.
- Do keep records of any permissions or
licenses you obtain—it’s your safety net in case of disputes.
- Do understand fair use—limited use for education,
commentary, or parody may be allowed, but it’s not a free pass.
10 ❌ Copyright Don’ts
- Don’t copy or share copyrighted
material without
permission, even if it’s just for a school project or social media post.
- Don’t assume everything online is
free to use—most
content is protected, even if it doesn’t have a copyright notice.
- Don’t modify or remix someone’s
work without
checking if you’re allowed to—it could still be infringement.
- Don’t use pirated software, music,
or movies—it’s illegal
and unethical.
- Don’t ignore takedown notices—they’re serious and could lead to
legal action if not addressed.
20 Copyright Dos and Don’ts When Dealing With Protected
Works
If
you're looking to protect your creative work online, there are several powerful
tools designed to detect copyright infringement. These tools use technologies
like content fingerprinting, reverse image search, and AI-driven pattern
recognition to spot unauthorized use. Here are some standout options:
11. 🛠️ Popular Copyright Detection
Tools : These
tools are especially useful for creators, educators, businesses, and platforms
that want to stay compliant and protect their intellectual property
- Red Points: Specializes in detecting and
removing copyright-infringing content across websites, marketplaces, and
social media platforms.
- ScoreDetect: Offers a suite of tools
including content fingerprinting, plagiarism detection, and digital
watermarking to monitor and protect your work.
- Videntifier: Uses advanced image and video
recognition to identify unauthorized use of visual content.
- DMCA.com Protection Services: Provides monitoring and takedown
services for websites using your content without permission.
- Google Reverse Image Search: A free and simple way to check
if your images are being used elsewhere online.
12. 📣 Why Public Awareness Matters
Despite
its benefits, many people still don’t understand how CC licensing works. That’s
where public awareness comes in:
- Educators and students can legally use CC-licensed
materials in classrooms and projects.
- Artists and creators can collaborate more freely
and build on each other’s work.
- Governments and institutions can promote open access to
knowledge and culture.
In
India, organizations like Wikimedia India and the Centre for Internet &
Society are actively working to raise awareness and promote the use of Creative
Commons in education and public policy.
Conclusion :
Copyright is a legal framework that gives creators of original works—like books, music, films, software, and artwork—the exclusive right to use, reproduce, distribute, and adapt their creations for a certain period of time. It’s a form of intellectual property protection that helps ensure artists and authors can benefit from their work. Here’s a quick breakdown of what copyright typically covers:
Reproduction rights (copying the work)
Distribution rights (selling or sharing copies)
Derivative works (like adaptations or translations)
Public performance and display (like playing music or showing films)
In most countries, copyright protection begins automatically as soon as the work is created and fixed in a tangible form—no registration needed. However, registering your copyright can make it easier to enforce your rights in court. In India, the governing law is the Copyright Act of 1957, which has been amended several times to keep up with digital and international developments.
 BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.
BLOG FOCUS-
COUNTRY FIRST,HEALTH & HYGIENE,GRATITUDE / VALUES, NOTHING IS FREE (work Hard) ENVIRONMENT, ROAD SAFETY & TRAFFIC RULES, LANGUAGE, SCIENTIFIC TEMPERAMENT & LIFE SKILLS.



.jpeg)



.jpeg)









